Curricula. Training preparation & planning process
Category: Training
Elaboration of the training agenda
The training curriculum defines the following:
course objectives
topics to be covered and their respective learning objectives
training methodologies
duration of the course
target audience
course schedule
The training curriculum establishes the framework by which you will develop your course materials, identify appropriate speakers, and set up the timing of your course.
It will also help you to determine how much it will cost to develop and deliver the training course.
• Course objectives
Why am I here?
What benefits will I receive?
Which of my needs will be met?
What is expected of me?
• Topics
The training agenda should list what subjects will be covered and the objectives to be achieved.
Topics can be divided by modules and sub-topics can be identified within each module.
• Length of workshop or course
Pay special attention to the timing demands of the intended audience:
Will they have to travel?
When will they be able to arrive?
Can they take the whole week off from their jobs?
Will they be able to work at night?
Will they be able to extract themselves from their daily responsibilities and focus exclusively on the course?
• Target audience
Specify who the workshop is intended for:
What is their background/experience?
What is the appropriate size of the group?
Should the group be homogeneous?
How much time can they commit?
Who will authorize their participation?
• Timing
What are the dates the course will take place?
At what time does each module begin and end?
Allocate time for coffee breaks, meals, cigarette breaks or other breaks depending on audience needs.
If you do not allow people time to take care of their personal needs you will notice a significant decline in their attention levels.
Modification of Materials
Making adjustments before training
To channel some persons into other training programs?
To adjust the course material?
Additional exercises for higher skilled attendees?
Making quick adjustments during training
To use warm-up exercises («ice-breakers»)?
Changes must reflect requirements of the content, audience and/or situation rather than instructor preferences
Changes — must make sense and must be appropriate
Substitute local cases, critical incidents, information, data, and experiences
If there is need for major changes — postpone the training
Judging the appropriateness and adequacy of any adjustment
Are the objectives still being met?
Did the adjustments solve the problem or improve the training?
Are the adjustments positively or negatively affecting learners?
Is there still a match with the training site?
Use of media & technology
Training Tools and Equipment
Tables, Desks, and Chairs
Sound Equipment
Computer Equipment
Overhead and LCD Projectors
Screen
Videocassette Recorder (VCR) with Television
Name Badges and Tent Cards
Notepads and Pencils
Podium or Lectern
Flipcharts and Markers
Whiteboard/Markers/Eraser
Water Pitcher and Glasses
b. Room layout
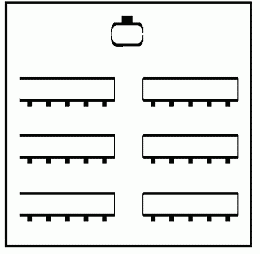
• Room Layout — Classroom
This layout allows participants to both take notes and participate in group exercises. Not good for plenary discussion.
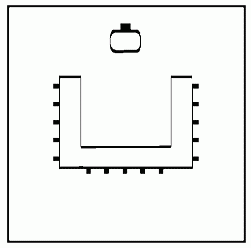
• Room Layout — U-Shaped/Closed Square
This more informal setting for smaller groups allows participants to take notes and participate in group discussions. This layout encourages greater participation
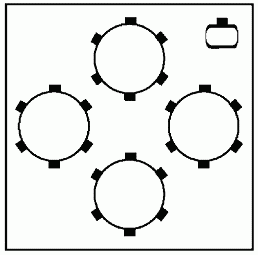
• Room Layout — Roundtable
This layout works best when group exercises are a major portion of the training meeting
• Room Layout — Conference
This layout encourages discussion while allowing participants to take the central role in activities
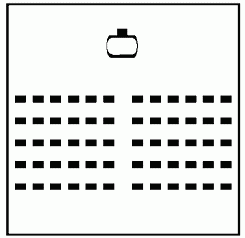
• Room Layout — Theater
This layout is appropriate for large plenary sessions
• Room Layout — Herringbone
This setting allows participants sitting in the back of the room to have improved sight lines and feel more involved in training
Costing Issues
Training assignments budgets must be based upon estimated attendance, with a sufficient reserve to allow for the unexpected.
It may be helpful to work with an training assignments budget committee to prepare the training budget and monitor expenditures. The budget should be based on anticipated revenues, such as registration fees, and estimated expenditures, such as the venue rental, printing of materials, and mailings. Use registration figures and the expenses from past training assignments to guide your planning.
Costs elements of a seminar
— Direct labor expenses
— Overhead expenses
— Direct expenses
— Profit
Relevant variables
— Program duration
— Quantity and quality of training materials
— Nr. of participants
— Time / day of the week
— Location