Supply and demand
Category: Marketing
For some products, such as raw materials, a company will accept the market prices since the product would not be bought at a higher price. A lower price on the other hand would not make sense either, since buyers are willing to pay the market price.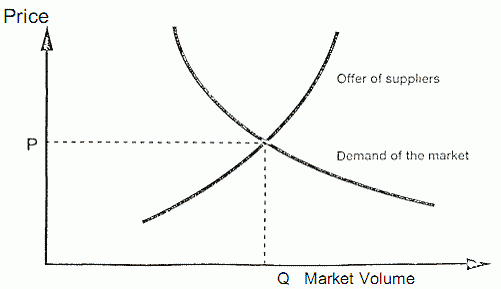
For a wide variety of product that, unlike raw materials, are distinguishable, there can be many reasons to ask a price that is different to the market price.
A lower than market price can be chosen if a company wants to gain market shares. In this market penetration strategy companies surrender some for the profit possible in order to gain long-term profitability through high market shares.
In this strategy, companies build up high capacities and set a price below market price. Thus, they gain market shares. Due to the higher volume their costs fall and prices can be lowered further. Finally, the company has low costs and dominates the market so that profits can be achieved.
A low price may also be feasible if attractive follow-up orders are expected. Low prices however might be regarded as a sign of low quality, so they should be accompanied by other marketing instruments.
In the long run, however, the prices have to cover all costs. In the short term, at least the variable costs should be covered. Therefore, costs set a minimum boundary for prices.
Higher than market prices can be asked if the product differs from competitors’ offers. A high price as part of the marketing mix can be obtained if the product can be established as a premium product with superior quality.
Example of elasticity of the demand
Enterprise X is producing very famous tractors. t uses perceived value to set prices on its construe on equipment
It might price its tractor at $100,000, although a similar competitor’s tractor might be priced at $90,000. And Enterprise X will obtain higher sales than the competitor!
When a prospective customer asks a X dealer why he should pay $10 000 more for the X tractor the dealer answers:
$ 90,000 is the tractor’s price if it is only equivalent to the competitor’stractor
$ 7,000 is the price premium for superior durability
$ 6,000 is the price premium for superior reliability
$ 5,000 is the price premium for superior service
$ 2,000 is the price premium for the loner warranty on parts
$ 110,000 is the price to cover the value package
$ 10,000 discount
$ 100,000 is the final price
The stunned customer learns that although he is asked to pay a $10 000 premium for the X tractor, he is actually getting a $10,000 discount! He ends up choosing the X tractor because he is convinced that its lifetime operating costs will be lower.
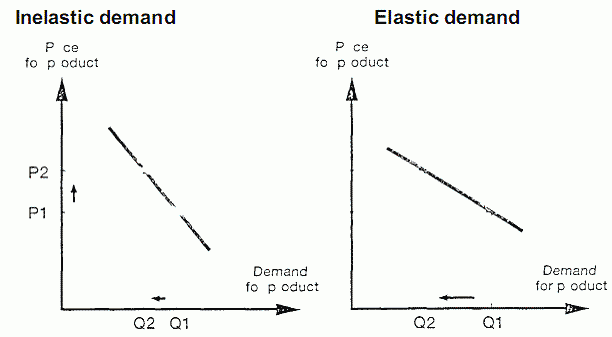
Impact of elasticity on prices
For products with inelastic demand the demand does not change much with prices. For elastic demand cases the demand depends strongly on the products prices.
| The product is more unique | Unique value effect |
| They are less aware of substitutes | Substitute awareness effect |
| They cannot easily compare the quality of substitutes | Difficult comparison effect |
| The expenditure is low compared to their income | Total expenditure effect |
| The expenditure is low compared to total cost of the project | End benefit effect |
| The product is assumed to have more quality, prestige, etc. | Price quality |
| The cannot store the product | Inventory effect |