CREDIT DEFAULT PRODUCTS
Category: Risk Management in Banking
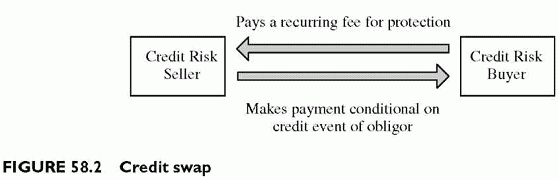
These include credit default swaps, credit default options or indemnity agreements. Conceptually, they are insurance products. The protection buyer looks for insurance in the event of default of the underlying. The seller requires a premium, and/or a periodic fee, for this service.
Although the word swap is used, these products look more like options. The payout of these contracts is a predetermined amount: a percentage of the face value of a loan, or a post-default difference between the pre-default bond price and the post-default bond price. The payment is contingent on the default event of an obligor (Figure 58.2).
Default events are specific in that the amount to be paid depends on recovery value post-default. Such a recovery percentage ranges from around 20% for unsecured facilities to 60% and above for secured ones. However, due to recovery risk, this amount is uncertain. Contracts are subject to basis risk since they pay something that might differ from actual recoveries. This is the case for loans, and less so for tradable bonds, since the post-default price exists. Credit events are also specific since they are subject to a variety of covenants that, if breached, trigger a default event.